
Effective Ways to Modify Your Gastroparesis Diet for Better Digestion in 2025
“`html
Effective Ways to Modify Your Gastroparesis Diet for Better Digestion in 2025
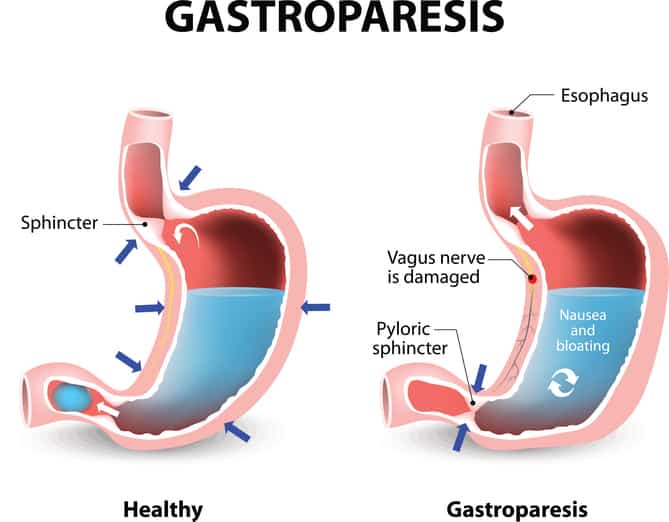

Understanding Gastroparesis and Dietary Modifications
Gastroparesis is a condition characterized by delayed stomach emptying, which can lead to various digestive challenges. Modifying your gastroparesis diet is crucial for effective symptom management and overall health. Emerging dietary approaches for 2025 focus on easily digestible foods, low fiber diets, and meal frequency adjustments. By adopting specific dietary modifications for gastroparesis, patients can experience improved digestion, reduced discomfort, and enhanced nutritional intake.
The Importance of Small Frequent Meals
One of the best strategies for managing gastroparesis is consuming small frequent meals throughout the day. Instead of three large meals, smaller portions can aid in digestion by reducing the burden on the stomach. This approach minimizes symptoms such as bloating and nausea, improving overall eating comfort. Try to space meals about every two to three hours, making sure they are balanced with proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. Adopting this habit not only helps in managing hunger but also plays a significant role in boosting calorie intake without overwhelming the digestive system.
Choosing the Right Foods
Incorporating the right foods into your gastroparesis diet can drastically improve your overall well-being. Opt for **easily digestible foods** such as mashed potatoes, yogurt, and well-cooked vegetables. It’s important to stay away from tough meats and high-fiber choices, which may trigger symptoms. Consider low-fat foods that are gentle on the stomach, focusing on nutrient-rich options. Additionally, exploring **gluten-free options** and low-carb diets might suit some individuals better and aid in symptom relief.
Meal Planning and Preparation Techniques
Effectively planning meals can decrease stress related to eating with gastroparesis. Start by engaging in **meal planning for gastroparesis** that accounts for personal preferences and symptom triggers. Utilizing cooking techniques such as blending or pureeing can create palatable and digestible meals. Try using the slow cooker to make stews with a variety of nutrients or whip up delicious chicken soup, which not only supports hydration but also offers dietary nourishment through its rich broth. Experimenting with **cooking techniques for gastroparesis** can transform how you view food while simplifying meal preparation.
Maintaining Nutritional Balance
Ensuring a balanced diet is vital for those with gastroparesis, primarily to avoid nutrient deficiencies and maintain overall wellness. The gastroparesis diet should not only alleviate symptoms but also meet **nutritional needs** effectively. Integrating supplements, especially vitamins that are critical for digestion, can help compensate for any dietary shortcomings.
Evolving Nutritional Needs
As symptom management may warrant special dietary transitions, understanding your body’s changing **nutritional needs** is crucial. Regular assessments, ideally with a registered dietitian, can help tailor a personalized nutrition plan. Vital nutrients like **Vitamin B12**, necessary for energy and cell production, can often be overlooked in individuals with this condition. Regular monitoring and adapting the gastroparesis diet can ensure no essential nutrient goes missing, supporting overall health in a manageable way.
The Role of Probiotics for Gut Health
Incorporating probiotics into your gastroparesis diet can contribute positively to gut health. Healthy gut bacteria serve as a prime mediator of digestion and can sometimes enhance the body’s ability to manage symptoms. Fermented foods, such as lactose-free yogurt, can be a tasty way to increase beneficial bacteria in your digestive system. Probiotics might not only alleviate some digestive discomfort associated with gastroparesis but also help restore balance within the gut, leading to better nutrient absorption.
Managing Reflux and Other Symptoms
Reflux is a common symptom associated with gastroparesis, and implementing dietary strategies can directly impact its severity. People with gastroparesis should focus on **reflux prevention** by avoiding trigger foods, maintaining portion control, and refraining from heavy meals close to bedtime. Incorporating alkaline foods and maintaining proper **hydration strategies** can also lessen symptoms. Additionally, evaluating personal responses to different foods through a **symptom diary** will enable you to fine-tune your diet over time and help you identify which foods best suit your individual digestive system.
Practical Tips for Successful Dietary Modifications
Successful adjustments to dietary habits for managing gastroparesis require practical strategies that can accommodate an individual’s lifestyle and preferences. Integrating these small changes can lead to substantial improvements in digestive comfort.
Hydration and Fiber Management
Hydration plays a key role in digestion for those with gastroparesis. Aim to drink fluids consistently throughout the day, favoring liquids that are easy on the stomach like broths or smoothies. Proper hydration synergizes well with managing **fiber intake**, as high fiber can worsen symptoms for some individuals. For better digestion, consider low-residue foods that provide energy while keeping fiber levels appropriate. Being aware of how your body reacts to various forms of water and food can maximally support absorption.
Portion Control and Eating Slowly
Adopting portion control involves careful vigilance over serving sizes and meal frequency while practicing **eating slowly**. Mindfully enjoying meals can aid in the digestive process, preventing overloading the stomach. Set the goal to chew food thoroughly and take smaller bites, as this contributes to better digestive outcomes. Staying aware of when you are feeling full can help prevent discomfort that arises from eating too quickly or too much at once.
Consulting with a Dietitian
To create an effective gastroparesis diet that suits your personal health needs, it’s wise to consult with a dietitian experienced in digestive disorders. A registered professional can provide insights on meal planning, nutritional supplementation, and recipe modification, all tailored to your unique condition. Their expertise leads to a deeper understanding of **avoiding trigger foods** and maximizing nutrient intake, helping you maintain a balanced diet and manage symptoms effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Implement small, frequent meals to improve digestion and comfort.
- Focus on easily digestible and low-fat foods to alleviate symptoms.
- Hydration is essential; consider low-residue and nutrient-rich diets.
- Monitor portion sizes and eating speed to help manage symptoms.
- Consult dietary professionals for personalized meal planning and guidance.
FAQ
1. What are some easily digestible foods for gastroparesis?
Some easily digestible foods include mashed potatoes, yogurt, soups, and smoothies. These options can reduce symptoms while providing necessary nutrients, ensuring you stay nourished without discomfort.
2. How important is portion control in a gastroparesis diet?
Portion control is crucial as it prevents overwhelming the stomach. Smaller portions allows for better digestion and minimizes bloating and nausea, which are often problematic for individuals with gastroparesis.
3. What role do probiotics play in managing gastroparesis?
Probiotics help with gut health by promoting a balanced microbiome and improving digestion. Including probiotic-rich foods, like lactose-free yogurt, can subtly enhance digestive comfort for those with gastroparesis.
4. Why is hydration an essential part of a gastroparesis diet?
Staying well-hydrated supports digestion and can help with symptoms commonly associated with gastroparesis. Keeping fluids in your diet can help your body manage nutrients more effectively and prevent constipation.
5. Can I use meal replacements under a gastroparesis diet?
Yes, meal replacements like nutritional shakes can be beneficial, as they provide necessary calories and nutrients without taxing the digestive system. Personalizing these options based on your nutrition analysis can help mitigate symptoms.
6. How often should I eat while managing gastroparesis?
It’s generally recommended to eat small meals every 2-3 hours. This can help manage overall caloric intake without overloading the stomach, ultimately reducing symptoms.
“`