Essential Guide to Gastroparesis Diet: Effective Options for 2025
Essential Guide to the Gastroparesis Diet: Effective Options for 2025
The **gastroparesis diet** is a critical aspect of managing the symptoms associated with this condition, which involves slow gastric emptying. This guide offers comprehensive insights into effective dietary options for individuals affected by gastroparesis, focusing on meal planning, food choices, and practical tips that ensure better digestive health in 2025.
Understanding Gastroparesis and Its Dietary Restrictions
Gastroparesis, characterized by chronic nausea and delayed gastric emptying, requires specific dietary modifications. Recognizing the importance of understanding gastroparesis can greatly improve symptom management. One essential aspect is avoiding **high volume meals**, as they can lead to discomfort. Instead, integrating **small frequent meals** helps alleviate symptoms associated with excess food intake. It’s also crucial to monitor **food triggers** and have **meal strategies** in place that optimize digestion and promote nutrient absorption.
Symptoms and Nutritional Considerations
Symptoms of gastroparesis often include nausea, bloating, and early satiety. Addressing these symptoms starts with understanding the **digestion of proteins** and the overall **fiber intake in gastroparesis**. High-fiber foods can exacerbate digestive issues; hence, adopting a **low-fiber diet** is generally recommended. Focusing on **easily digestible foods** that provide necessary nutrients without overwhelming the stomach becomes paramount. For instance, incorporating **gastroparesis-friendly vegetables** such as carrots and leafy greens in their soft-cooked form is beneficial.
Dietary Guidelines for Gastroparesis Management
Proper **hydration** is key in managing gastroparesis symptoms. Hydration tips include drinking fluids between meals rather than during and choosing **liquid diets for gastroparesis** when warranted. **Nutritional supplements for gastroparesis** can also help meet dietary needs, particularly if there’s difficulty consuming sufficient calories. For those managing gastroparesis and diabetes, it’s essential to monitor **sugar content in the diet** and incorporate **low-fat diet** practices that will maintain energy levels without overwhelming the digestive system.
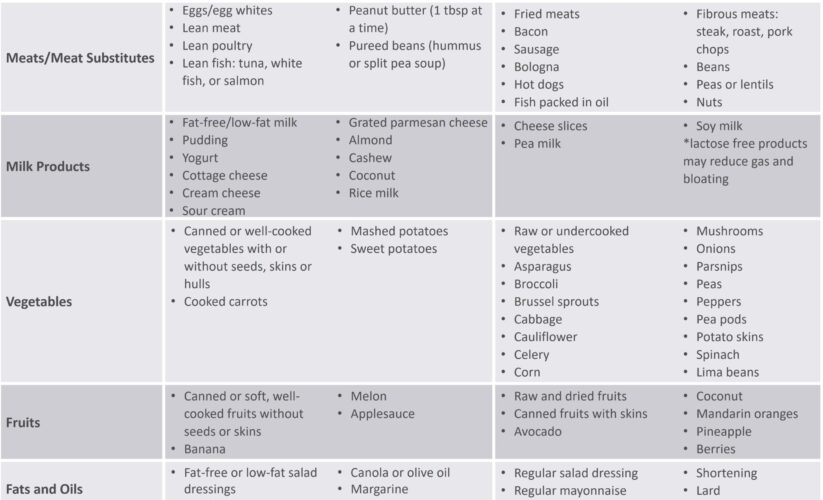
Creating a Gastroparesis Food List
Compiling a **gastroparesis food list** with appropriate options ensures greater dietary adherence and nutritional balance. Understanding which foods to avoid is equally important for effective management. Foods that are typically unsuitable include raw fruits and vegetables, tough meats, and high-fat dairy products. Instead, focusing on soft foods for gastroparesis such as pureed fruits, oatmeal, and well-cooked proteins will offer the nutrients required while minimizing gastrointestinal distress.
Gastroparesis Recipes and Meal Planning
Incorporating **gastroparesis recipes** into meal planning can enhance variety and flavor while adhering to dietary goals. Some simple, nutritious recipes include blended soups rich in **micronutrients**, smoothies with high-calorie content from healthy fats, and soft casseroles packed with protein. Exploring **meal timing** also plays a significant role; scheduled meals can help acclimate the digestive system to a routine, reducing fluctuations that lead to symptom discomfort.
Cooking Methods and Preparation Tips
Knowing **cooking methods for gastroparesis** can significantly impact food texture and digestibility. Techniques such as steaming, slow-cooking, or blending can make food easier on the stomach, while preserving nutrients. Moreover, implementing **meal texture modification** strategies can aid in better swallowing and digestion, ensuring that the meals are not only easier to consume but also pleasant to eat. Furthermore, incorporating **adjustable diet plans** that consider the individual’s changing tolerance levels encourages gradual adaptation to dietary needs.
Navigating Nutritional Supplements and Snacks
While whole foods are preferable, the use of **nutritional supplements for gastroparesis** can fill any dietary gaps. **Protein shakes** or meal replacement drinks can be beneficial, particularly when appetite is low or food intake is restricted due to symptoms. Additionally, High-calorie snacks can be included strategically throughout the day to ensure overall caloric intake meets individual needs without excessive volume, which can lead to discomfort.
Monitoring Hydration and Overall Health
Maintaining optimal hydration status is vital in the daily management of gastroparesis. Drinking fluids regularly, using **hydration tips** such as including electrolyte-rich drinks, can support proper digestive health. It’s also advised to track dietary intake for adjustments based on reactions to diverse foods. Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly is particularly essential for those with **gastroparesis and diabetes**, highlighting the need for awareness around dietary changes.
Family Involvement and Cooking Tips
Involving family members in meal preparation can ease the burden of cooking daily gastroparesis-friendly meals. Healthier cooking methods, acceptable food choices, and shared responsibilities around meal planning and preparation are vital for emotional support and improved quality of life. **Cooking tips for gastroparesis** can include the use of flavor enhancers without additional fats to promote enjoyment while maintaining adherence to dietary restrictions.
Key Takeaways for the Gastroparesis Diet in 2025
- Implement a **low-fiber diet** to minimize gastrointestinal discomfort while ensuring nutrient intake.
- Focus on **small frequent meals** and **high-calorie snacks** to maintain energy levels.
- Utilize **easy to digest foods** and understand the role of hydration and nutritional supplements.
- Engage in **meal planning** with **gastroparesis recipes** and involve family for more enjoyable meal preparation.
- Regularly monitor **hydration status** and food intake for better symptom management.
FAQ
1. What foods should I avoid on a gastroparesis diet?
When pursuing a gastroparesis diet, it’s crucial to avoid foods that can delay gastric emptying. Common foods to avoid include raw vegetables, tough meats, whole nuts, high-fat foods, and carbonated beverages. These can contribute to discomfort, bloating, and overall digestive distress, making it imperative to focus on **soft foods for gastroparesis**.
2. Is a low-residue diet beneficial for gastroparesis?
Yes, a **low-residue diet** can be beneficial for managing gastroparesis symptoms. This diet minimizes fiber intake from whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, facilitating easier digestion. By focusing on **low-fiber options**, individuals can enhance their comfort levels throughout their meals while ensuring essential nutrients are still accessed through appropriate selections of softer food choices.
3. How important is hydration in managing gastroparesis?
Hydration plays a vital role in **managing gastroparesis**, as adequate fluid intake aids in digestion and helps prevent constipation. Drinking clear liquids can facilitate smoother digestion, although it’s advised to drink fluids between meals rather than during to minimize feelings of fullness and allow for better digestion of solid foods.
4. What are some high-calorie snacks appropriate for gastroparesis?
High-calorie snacks that are appropriate for gastroparesis include protein shakes, smoothies, Greek yogurt, and peanut butter on soft bread. These snacks help increase caloric intake without overwhelming stomach capacity when adhering to a **diet for sensitive stomachs**.
5. How can I include my family in meal planning for gastroparesis?
Involving family in meal planning can provide support and alleviate the challenges of preparing meals for gastroparesis. Family members can assist by researching **gastroparesis recipes**, cooking together, and maintaining open communication regarding food preferences and intolerances. This collective approach can enhance mealtime experiences and provide emotional support.
6. Are there specific cooking methods that benefit digestion in gastroparesis?
Certain cooking methods are especially beneficial for gastritis, such as steaming, slow cooking, blending, and pureeing dishes. These techniques not only improve the food’s texture but also help maintain nutrient value while promoting easier digestion and absorption during meals.
7. What role do nutritional supplements play in a gastroparesis diet?
Nutritional supplements can play a significant role in a gastroparesis diet by filling nutritional gaps and ensuring adequate calorie intake, especially when solid foods pose a challenge. Supplements like meal replacement drinks or **protein shakes** allow individuals to obtain necessary nutrients without contributing to overstimulation of the digestive system.

